

The R package deepSTRAPP employs time-calibrated
phylogenies and trait data to test for differences in
diversification rates between traits over evolutionary time. It
works with continuous, categorical, and biogeographic trait data and
extends the STRAPP test from
[BAMMtools::traitDependentBAMM()] to any time step along
phylogenies.
deepSTRAPP provides a powerful analytic
framework to investigate the Diversification Rate Hypothesis
(DRH) in the context of Historical Biogeography. DRH posits
that current heterogeneity in diversity patterns such as the Latitudinal
Diversity Gradient are mostly due to differences in diversification
rates across bioregions. This hypothesis is typically assessed by
comparing diversification rates across tips between the different
bioregions with for example a STRAPP test (Rabosky & Huang,
2016). However, such tests only compare current rates of
diversification that may not be informative about the long-term
past dynamics shaping present-day biodiversity. deepSTRAPP
overcomes this methodological gap: it enables to test the DRH by
comparing diversification rates at any time step along
evolutionary time. As a typical outcome, it allows researchers
to identify time-frame of significance during which
diversification rates were different across trait values, providing a
quantitative testing framework to disentangle effects of past
and current dynamics in explaining current patterns of
biodiversity.
Beyond the biogeographic context, deepSTRAPP can be used to test for an evolutionary relationship between phenotypic evolution and diversification dynamics for any type of traits. It provides an alternative approach to state-dependent speciation and extinction (SSE) models that intend to model altogether trait evolution and diversification dynamics, but are often time-consuming and hard to parametrize, especially on large time-calibrated phylogenies. Thus, deepSTRAPP offers a flexible solution that can be applied to phylogenies encompassing thousands of lineages (Doré al., 2025).
deepSTRAPP is especially suited for large phylogenies as the power of the statistical tests is limited by the number of diversification regime shifts detected on the phylogeny and used to perform permutation tests. Each macroevolutionary regime acts as an independent event used to test for differences, therefore the sample size of the tests is conditioned by the number of macroevolutionary regimes identified. It is unlikely to detect any significant differences with few regime shifts.
A full deepSTRAPP workflow runs as follows:
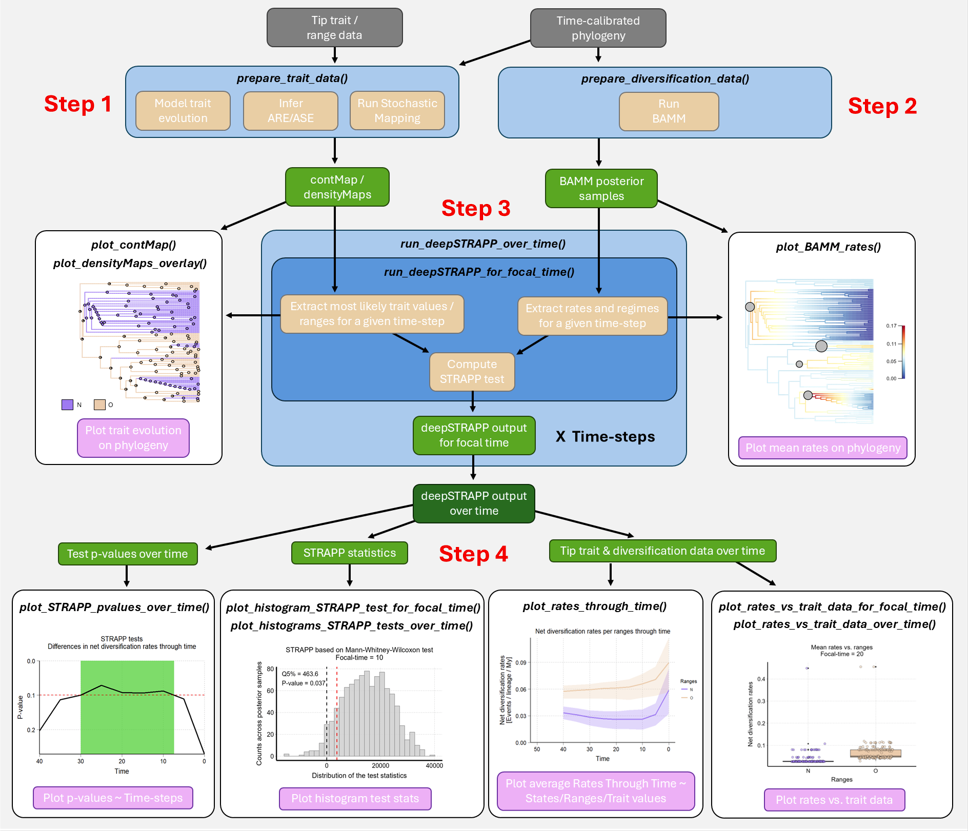 Figure 1: Simplified
deepSTRAPP workflow showing the main functions (in italics)
involved in each step. Input data in grey. Data processing in
blue (main) and beige (internal). Intermediate objects in green. Final
outputs in pink.
Figure 1: Simplified
deepSTRAPP workflow showing the main functions (in italics)
involved in each step. Input data in grey. Data processing in
blue (main) and beige (internal). Intermediate objects in green. Final
outputs in pink.
References:
STRAPP test: Rabosky, D. L., & Huang, H. (2016). A robust semi-parametric test for detecting trait-dependent diversification. Systematic biology, 65(2), 181-193. https://doi.org/10.1093/sysbio/syv066.
deepSTRAPP application: Doré, M., Borowiec, M. L., Branstetter, M. G., Camacho, G. P., Fisher, B. L., Longino, J. T., Ward, P. S., Blaimer, B. B. (2025). Evolutionary history of ponerine ants highlights how the timing of dispersal events shapes modern biodiversity. Nature Communications, 16, 8297. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-025-63709-3
deepSTRAPP works on R version 4.4 or more. Be sure to have an R
version that is compatible.
See https://CRAN.R-project.org/.
From CRAN, for the latest release:
install.packages("deepSTRAPP")From GitHub, for the current development version, including all example datasets:
library(devtools)
remotes::install_github(repo = "MaelDore/deepSTRAPP")You may need additional tools for package compilation such as Rtools
(Windows) and Xcode (Mac OS).
See this
page for details.
deepSTRAPP relies on other software and R packages to perform some of its core tasks. R package dependencies will automatically be downloaded and installed alongside deepSTRAPP. However, R packages that are not currently available on CRAN, and external software may need to be installed independently.
library(devtools)
devtools::install_github(repo="nmatzke/BioGeoBEARS")For more information, please refer to the official BioGeoBEARS Wiki.
Reference:
Matzke, Nicholas J. (2018). BioGeoBEARS: BioGeography with Bayesian (and likelihood) Evolutionary Analysis with R Scripts. version 1.1.1, published on GitHub on November 6, 2018. DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.1478250
Reference:
Rabosky, DL. Automatic detection of key innovations, rate shifts, and diversity-dependence on phylogenetic trees. PLoS One 9, e89543 (2014). DOI: https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0089543
A companion website is available to browse interactively the different tutorials and functions of deepSTRAPP at this URL: https://maeldore.github.io/deepSTRAPP/.
An overview of all functions and datasets is available here.
A simple use-case that shows how deepSTRAPP can be
used to test for differences in diversification rates between
two trait states along evolutionary times is available here
and within R: vignette("main_tutorial").
This tutorial presents the main functions in a typical
deepSTRAPP workflow.
For more advanced used,
please refer to the vignettes/tutorials below.
Tutorials are available to explore more advanced
usages of deepSTRAPP. They provide explanations on available
arguments and interpretations of results of deepSTRAPP across multiple
types of data. They are listed below, in the companion
website, and in this vignette:
vignette("deepSTRAPP").
1/ Full deepSTRAPP workflows on different types of data
vignette("deepSTRAPP_continuous_data").vignette("deepSTRAPP_categorical_data").vignette("deepSTRAPP_biogeographic_data").2/ Explore options for trait evolution
vignette("model_continuous_trait_evolution").vignette("model_categorical_trait_evolution").vignette("model_biogeographic_range_evolution").3/ Explore options for BAMM
vignette("model_diversification_dynamics").4/ Explore the STRAPP test options
Test
difference hypotheses:
vignette("explore_STRAPP_test_types").
5/ Plot rates through time (RTT)
vignette("plot_rates_through_time").6/ Cut phylogenies
Cut
different types of (mapped) phylogenies for a given
focal-time: vignette("cut_phylogenies").
Alternatively, if you prefer to view the vignettes in R, you can
install the package with build_vignettes = TRUE. But be
aware that some vignettes can be slow to generate.
remotes::install_github(repo = "MaelDore/deepSTRAPP",
dependencies = TRUE,
upgrade = "ask",
# Time-consuming, but needed if you want to have access to the vignettes/tutorials
build_vignettes = TRUE)
# Access vignettes within R
vignette("deepSTRAPP")
# You can also use this to open access to all local vignettes in an HTML Brower
utils::browseVignettes(package = "deepSTRAPP")Thank you for finding it! Head over to the GitHub Issues
tab and let me know about it.
You can also
send me an e-mail.
For any use of deepSTRAPP:
Doré, M., & Blaimer, B. B., deepSTRAPP: Testing for differences in diversification rates over deep evolutionary time. (DOI TBA)
As deepSTRAPP relies strongly on functions designed for the phytools R package, it is good practice to also cite this package:
Revell, L. J. (2024) phytools 2.0: an updated R ecosystem for phylogenetic comparative methods (and other things). PeerJ, 12, e16505. https://doi.org/10.7717/peerj.16505.
If you use the modeling tools for trait evolution embedded in the function prepare_trait_data(), you should cite the R package geiger:
Pennell, M.W., J.M. Eastman, G.J. Slater, J.W. Brown, J.C. Uyeda, R.G. FitzJohn, M.E. Alfaro, and L.J. Harmon. 2014. geiger v2.0: an expanded suite of methods for fitting macroevolutionary models to phylogenetic trees. Bioinformatics 30:2216-2218. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btu181.
If you use the modeling tools for historical biogeography embedded in the function prepare_trait_data(), you should cite the R package BioGeoBEARS:
Matzke, N. J. (2013). Probabilistic historical biogeography: new models for founder-event speciation, imperfect detection, and fossils allow improved accuracy and model-testing. Frontiers of Biogeography, 5(4). https://doi.org/10.21425/F5FBG19694.